Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Manufacturing
In today’s ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the call for sustainable practices has risen beyond a mere catchphrase, transforming into an urgent mandate for industries across the globe. As the world grapples with mounting apprehensions regarding the depletion of natural resources and environmental decline, the imperative to reevaluate and revolutionize conventional manufacturing methodologies looms larger than ever before (Hamia et al., 2015).
Sustainability in manufacturing signifies an evolution from the conventional paradigms of production. It encompasses a comprehensive approach aimed at minimizing environmental impact, optimizing resource utilization, and fostering economic resilience. As consumers demand eco-friendly products and regulatory frameworks become more stringent, manufacturers are compelled to reassess their practices to align with sustainability objectives. This entails more than mere token gestures, it necessitates a fundamental shift in how products are conceptualized, designed, produced, and disposed of.
Understanding Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainable manufacturing represents a significant departure from conventional production paradigms, encompassing dimensions beyond mere profit considerations to include environmental and societal well-being (Hamia et al., 2015). At its essence, sustainable manufacturing seeks to achieve a delicate equilibrium between economic prosperity, environmental preservation, and societal advancement. This involves not only curtailing resource depletion, pollution, and waste generation but also fostering innovation, economic growth, and the overall welfare of communities. Achieving these goals necessitates optimizing material utilization, minimizing energy consumption, and embracing cleaner and more sustainable production processes.
In an era marked by rapid transformation, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into manufacturing offers promising potential to pave the way toward a more sustainable future. By comprehending the transformative influence of AI on various facets of manufacturing operations, we lay the foundation for discussions that transcend the realms of technological adoption alone.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in various industries, and manufacturing is no exception. It is a multidisciplinary field encompassing machine learning, robotics, and data analysis, and has demonstrated its prowess in processing vast amounts of data and deriving actionable insights. This capacity for real-time analysis and optimization renders AI an invaluable tool in the context of manufacturing, poised to reshape the industry on a fundamental level.
In modern manufacturing, the demand for meeting throughput, quality, and cost objectives while ensuring sustainability presents challenges. AI offers unique capabilities, especially in problem-solving, by identifying intricate patterns within vast datasets generated by machines, sensors, and controllers. These data categories range from environmental data to production operation records, creating opportunities for pattern discovery. This capability enhances root cause analysis and offers insights into system behavior, aligning with the hierarchical approach to manufacturing systems (Arinez et al., 2020).
However, the impact extends beyond operations, addressing long-standing industry challenges. Balancing cost-effective production with environmental sustainability is a prime concern. AI’s predictive prowess optimizes processes while minimizing resource waste, aligning with eco-friendly practices. This convergence of efficiency and sustainability aligns with the call for greener manufacturing.
Moreover, AI’s insights transcend the product lifecycle, from raw material sourcing to disposal. By identifying recycling, repurposing, and reusing opportunities, AI fosters a circular economy within manufacturing, minimizing waste and supporting sustainable production.
As manufacturing navigates a future of resource scarcity and environmental accountability, AI illuminates the path forward. Beyond profitability, AI empowers manufacturers to become stewards of sustainability, transcending traditional roles and prompting a fundamental industry transformation. This evolution is guided by AI’s ability to understand complex data patterns, adapt processes, and provide informed decision-making, securing its place as a catalyst for lasting change.
Enhancing Sustainability Through AI-Driven Applications
While machine learning has demonstrated its potential to enhance manufacturing processes, it’s essential to acknowledge that it might not be universally applicable to all manufacturing contexts. ML shines in analyzing complex processes with interrelated parameters and offering predictive insights, yet there are instances where simpler non-ML methods remain effective and practical. The decision between the two approaches hinges on factors such as the need for additional insights and the availability of expertise.
Interestingly, despite the growing role of AI in manufacturing, there exists a noticeable gap in the literature concerning its specific contributions to sustainability enhancement. While AI applications have shown promise in multiple domains, the discussion about how AI can comprehensively contribute to sustainability within manufacturing is still relatively limited. This gap calls for further exploration and research to uncover AI’s full potential in advancing sustainable manufacturing practices.
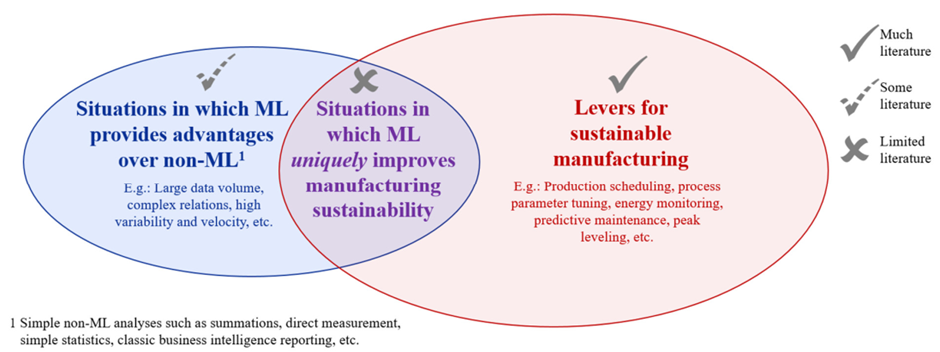
In the pursuit of harnessing the full potential of AI in manufacturing, it’s crucial to delve into the specific avenues through which AI-driven applications can bolster sustainability. These applications present opportunities to not only enhance operational efficiency but also to make substantial strides toward minimizing the environmental footprint of manufacturing processes. By incorporating AI’s analytical capabilities, manufacturers can unlock new dimensions of sustainability, optimize resource usage, reduce waste, and advance eco-friendly practices.
The integration of AI into manufacturing processes opens a realm of possibilities, each contributing to the overarching goal of sustainability. There are several applications of AI that can increase sustainability, such as process parameters optimization, predictive maintenance, efficient logistics management, predictive quality assurance, and intelligent scheduling to create a harmonious ecosystem of efficiency and environmental responsibility (Ekwaro-Osire et al., 2022). Let’s explore these key domains where AI’s influence is transforming the landscape of sustainable manufacturing.
- Process Parameters Optimization: AI brings a level of precision to manufacturing that was previously unattainable. By analyzing real-time data and identifying intricate patterns, AI optimizes process parameters. This minimizes resource waste, enhances product quality, and reduces energy consumption. Manufacturers can achieve more with less, aligning with the principles of sustainable manufacturing.
- Predictive Maintenance: Unplanned downtime due to equipment breakdowns contributes to inefficiency and environmental strain. AI’s predictive maintenance capabilities pre-emptively identify potential issues. By detecting subtle changes in equipment behavior, AI-driven systems enable timely interventions, extending equipment lifespans, and minimizing waste through resourceful maintenance.
- In- and Outbound Logistics: Efficient logistics is a cornerstone of sustainable manufacturing. AI optimizes inbound and outbound logistics, ensuring that resources and products are transported with precision timing. This not only reduces transportation emissions but also aligns with lean production principles, minimizing excess inventory and waste.
- Predictive Quality Assurance: AI’s predictive capabilities extend beyond maintenance to quality assurance. By analyzing historical and real-time data, AI can predict product defects before they occur. Manufacturers can pre-emptively address quality issues, reducing waste from subpar products and enhancing overall product excellence.
- Smart Scheduling: Intelligent scheduling is an integral part of sustainable manufacturing. AI analyses a multitude of variables to create optimal production schedules. This minimizes idle time, reduces energy consumption, and streamlines resource utilization, ensuring that every aspect of production contributes to sustainability goals.
These applications exemplify how AI acts as a catalyst for sustainability in manufacturing. By seamlessly integrating AI into these core aspects, we unlock a powerful arsenal of tools that not only optimize operations but also minimize resource waste and environmental impact. Process parameters optimization ensures that every action aligns with energy efficiency, resulting in a production process that maximizes output while minimizing input. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI’s ability to anticipate machinery needs, leads to proactive interventions, reducing unplanned downtime and the accompanying energy wastage.
Efficient logistics management, guided by AI’s real-time analysis, transforms the movement of resources and goods into a well-orchestrated symphony. This not only cuts down transportation emissions but also streamlines supply chains, minimizing excess inventory and waste. Quality assurance, backed by predictive insights, safeguards against defects, reducing the need for rework and curbing material waste. In the realm of intelligent scheduling, AI’s intricate algorithms pave the way for resource-efficient production timelines, where energy-intensive processes align seamlessly with peak demand.
Conclusion
The fusion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and sustainable manufacturing has illuminated a path toward a future where efficiency, innovation, and environmental stewardship converge. In this analysis, we’ve journeyed through the symbiotic relationship between AI and manufacturing processes, uncovering how AI serves as a driving force for sustainability across various dimensions.
The transformative potential of AI in manufacturing is undeniable. From optimizing process parameters and predictive maintenance to efficient logistics management and intelligent scheduling, AI applications amplify efficiency while minimizing resource waste and environmental impact. The intricate dance between AI and sustainable manufacturing offers manufacturers the ability to balance economic growth with responsible resource utilization.
AI-driven sustainable manufacturing transcends theoretical musings, as real-world implementations continue to yield impressive results. Companies leveraging AI to optimize processes, reduce downtime, and enhance logistics efficiency have seen quantifiable improvements in their environmental footprint and operational profitability. As these success stories accumulate, they inspire a broader shift toward a manufacturing landscape that not only meets present demands but also safeguards the planet for future generations.
References
Ekwaro-Osire, H., Bode, D., Thoben, K.-D., & Ohlendorf, J.-H. (2022). Identification of Machine Learning Relevant Energy and Resource Manufacturing Efficiency Levers. Sustainability, 14(23), 15618. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315618
Hamia, N., Muhamad, M. R., & Ebrahim, Z. (2015). The Impact of Sustainable Manufacturing Practices and Innovation Performance on Economic Sustainability. Procedia CIRP, 26, 190-195.
Arinez, J. F., Chang, Q., Gao, R. X., Xu, C., & Zhang, J. (2020). Artificial Intelligence in Advanced Manufacturing: Current Status and Future Outlook. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 142, 110804.